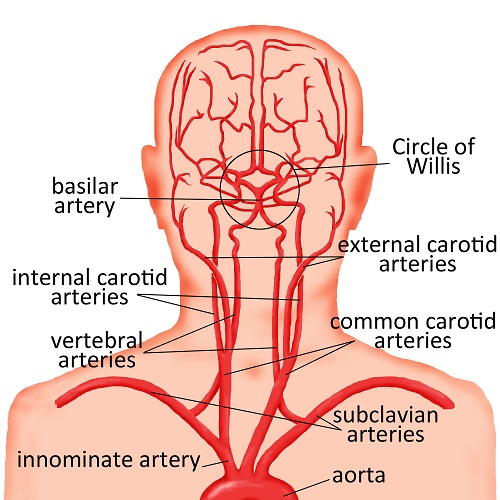
Sonographic (ultrasound) examination of carotid arteries, or extracranial (neck) arteries of the brain, is a non-invasive examination that may reveal the presence of a narrowing or occlusion of the artery. This state is called a stenosis and may affect the blood flow rate in the arteries. The examination also allows to assess the severity of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) in the examined patient.
Examination of the carotid arteries is very important in determining the risk of stroke (cerebral infarction) in patients where the carotid artery is narrowed by more than 70%.
Also, patients who have had a stroke should be monitored and given the right treatment to prevent a recurrence of the stroke and to prevent further narrowing of the carotid arteries.
Also, patients who have had a stroke should be monitored and given the right treatment to prevent a recurrence of the stroke and to prevent further narrowing of the carotid arteries.
The examination should be done to every patient:
- with high blood pressure
- with diabetes mellitus
- smoker
- with high levels of cholesterol and other fats in the blood
- with known ischemic heart disease (eg. after a heart attack)
- with known limb artery disease (PAOD)
- with neurological symptoms (limb movement disorder, impaired speech, after stroke)
- with sudden loss of visual field in one eye (amaurosis)